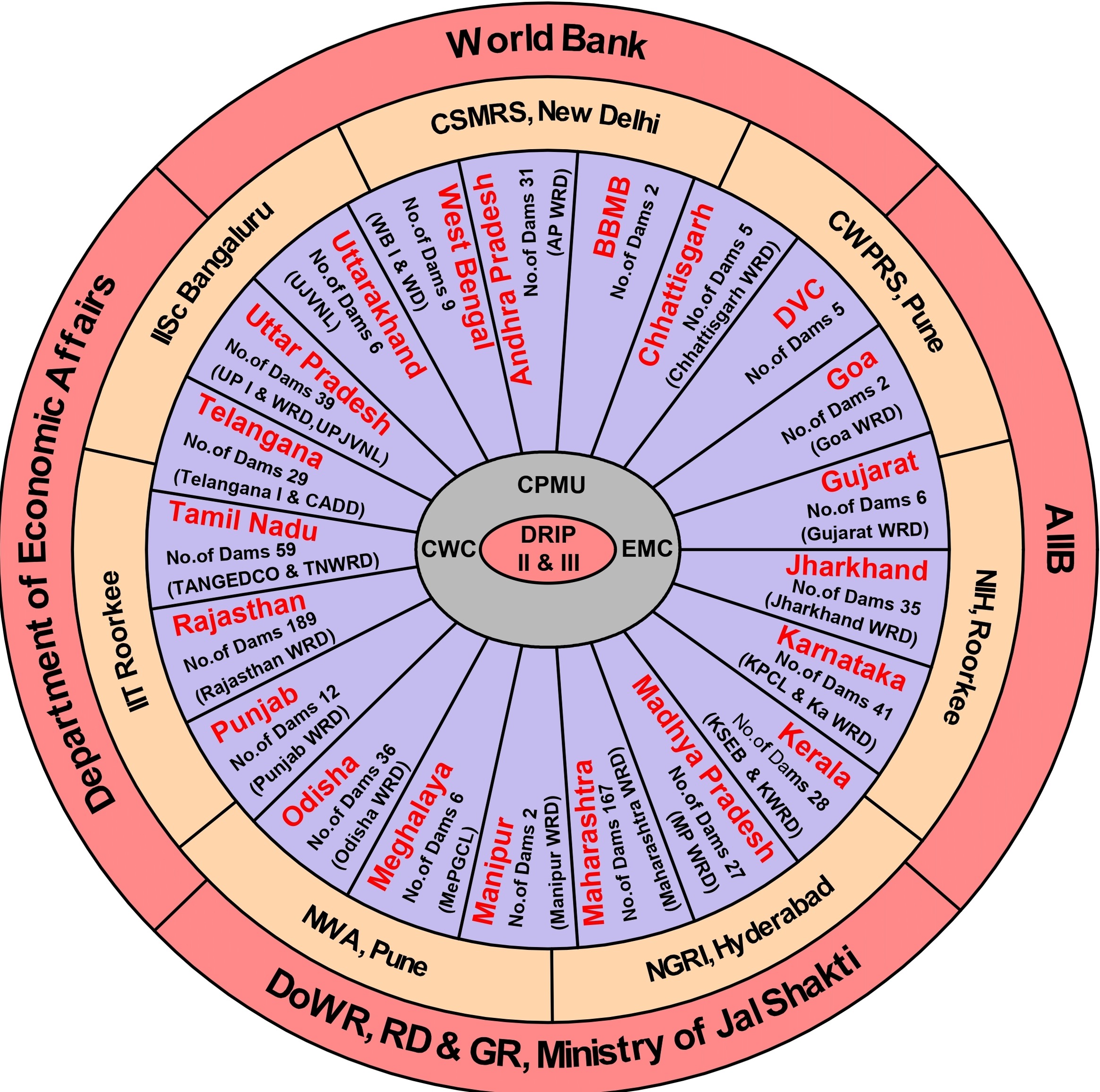
India is home to some of the world's most sizeable river diversion infrastructure and ranks third after China and the United States in terms of number of large dams. As per National Register of Specified Dam 2025, India owns portfolio of 6628 dams (6545 operational and 83 under construction). These dams are vital for ensuring the water security of the country and constitute a major responsibility in terms of asset management and safety. The Department of Water Resources, River Development and Ganga Rejuvenation through Central Water Commission (CWC) is coordinating and supervising implementation of Dam Rehabilitation and Improvement Project (DRIP) Phase II and III, with financial assistance from the World Bank and Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank. The Project Development Objective is to increase the safety of selected dams in participating States and to strengthen dam safety management in India through institutional strengthening.
This Scheme is a continuing Scheme of DRIP-I, which was implemented during April 2012 to March 2021.Under DRIP-1, physical rehabilitation of 223 dams have been completed at cost of Rs 2567 Cr based on the outcomes of Design Flood review and Inspection by Dam Safety Review Panels. In addition to physical rehabilitation, various other Dam Safety Institutional Strengthening measures were undertaken including publication of Guidelines/Manuals, capacity building of 8 academic and 2 central agencies; publication of dam specific EAPs and O&M Manuals, capacity building or various stakeholders wherein about 5500 officers have been trained on various domains of dam safety etc